| Target Namespace | http://www.witsml.org/schemas/131/addendum/combo |
|---|---|
| Version | 1.3.1 |
| Element and Attribute Namespaces |
|
| Schema Composition |
|
| Prefix | Namespace |
|---|---|
| witsml | http://www.witsml.org/schemas/131/addendum/combo |
| xml | http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace |
| xsd | http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema |
| Super-types: | None |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
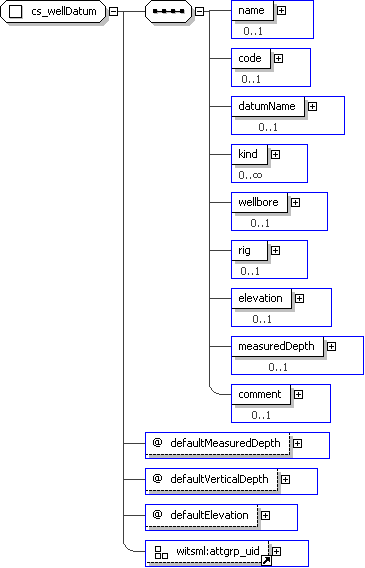
| Name | cs_wellDatum |
|---|---|
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | Defines the datums associated with elevation, vertical depth and measured depth coordinates within the context of a well. |
'True indicates that this is the default reference datum for measured depth coordinates. False or not given indicates that this is not the default reference datum. Measured depth coordinates that do not specify a datum reference should be assumed to be measured relative to this default reference datum. Only one reference datum may be designated as the default measured depth datum for each well. Values are \"true\" (or \"1\") and \"false\" ( or \"0\").'
"'True indicates that this is the default reference datum for vertical depth coordinates. False or not given indicates that this is not the default reference datum. Vertical depth coordinates that do not specify a datum reference should be assumed to be measured relative to the default reference datum. Only one reference datum may be designated as the default vertical depth datum for each well. Values are \"true\" (or \"1\") and \"false\" ( or \"0\").'
"'True indicates that this is the default reference datum for elevation coordinates. False or not given indicates that this is not the default reference datum. Elevation coordinates that do not specify a datum reference should be assumed to be measured relative to the default reference datum. Only one reference datum may be designated as the default elevation datum for each well. Values are \"true\" (or \"1\") and \"false\" ( or \"0\").'
"'The unique identifier of a container element. This attribute is generally required within the context of a WITSML server. There should be no assumption as to the semantic content of this attribute. This should only be used with recurring container types (i.e., maxOccurs greater than one). The value is only required to be unique within the context of the nearest recurring parent element.'
">'The human understandable contextual name of the reference datum.'
'The code value that represents the type of reference datum. This may represent a point on a device (e.g., kelly bushing) or it may represent a vertical reference datum (e.g., mean sea level).'
'The name of the vertical reference datum in a particular naming system. This should only be specified if the above \'code\' represents some variation of sea level. An optional short name (code) can also be specified. Specifying a well known datum is highly desired if the above code is a variant of sea level because sea level varies over time and space. An example would be to specify a name of \'Caspian Sea\' with a code of \'5106\' in the \'EPSG\' naming system.'
'Since various activities may use different points as measurement datums, it is useful to characterize the point based on its usage. A well reference datum may have more than one such characterization. For example, it may be the datum used by the driller and logger for measuring their depths. Example usage values would be \'permanent\',\'driller\', \'logger\' \'WRP\' (well reference point) and \'SRP\' (site reference point).'
'A pointer to the wellbore that contains the reference datum. This should be specified if a measured depth is given.'
'A pointer to the rig that contains the device used as a reference datum. The rig may be associated with a wellbore in another well (e.g., pattern drilling using a rig on a track).'
'The gravity based elevation coordinate of this reference datum as measured from another datum. Positive moving upward from the elevation datum. An elevation should be given unless this is a vertical reference datum (e.g., sea level).'
'The measured depth coordinate of this reference datum as measured from another datum. The measured depth datum should either be the same as the elevation datum or it should be relatable to the elevation datum through other datums. Positive moving toward the bottomhole from the measured depth datum. This should be given when a local reference is \"downhole\", such as a kickoff point or ocean bottom template, and the borehole may not be vertical. If a Depth is given then an Elevation should also be given.'
'A contextual description of the well reference datum.'

| Super-types: | Address < AusAddress (by extension) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: |
|
| Name | AusAddress |
|---|---|
| Abstract | no |
The XML Instance Representation table above shows the schema component's content as an XML instance.
Abstract (Applies to complex type definitions and element declarations). An abstract element or complex type cannot used to validate an element instance. If there is a reference to an abstract element, only element declarations that can substitute the abstract element can be used to validate the instance. For references to abstract type definitions, only derived types can be used.
All Model Group Child elements can be provided in any order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-all.
Choice Model Group Only one from the list of child elements and model groups can be provided in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-choice.
Collapse Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32). Then, collapse contiguous sequences of space characters into single space character, and remove leading and trailing space characters.
Disallowed Substitutions
(Applies to element declarations). If substitution is specified, then substitution group members cannot be used in place of the given element declaration to validate element instances. If derivation methods, e.g. extension, restriction, are specified, then the given element declaration will not validate element instances that have types derived from the element declaration's type using the specified derivation methods. Normally, element instances can override their declaration's type by specifying an xsi:type attribute.
Key Constraint Like Uniqueness Constraint, but additionally requires that the specified value(s) must be provided. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.
Key Reference Constraint Ensures that the specified value(s) must match value(s) from a Key Constraint or Uniqueness Constraint. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.
Model Group Groups together element content, specifying the order in which the element content can occur and the number of times the group of element content may be repeated. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#Model_Groups.
Nillable
(Applies to element declarations). If an element declaration is nillable, instances can use the xsi:nil attribute. The xsi:nil attribute is the boolean attribute, nil, from the http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance namespace. If an element instance has an xsi:nil attribute set to true, it can be left empty, even though its element declaration may have required content.
Notation A notation is used to identify the format of a piece of data. Values of elements and attributes that are of type, NOTATION, must come from the names of declared notations. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cNotation_Declarations.
Preserve Whitespace Policy Preserve whitespaces exactly as they appear in instances.
Prohibited Derivations (Applies to type definitions). Derivation methods that cannot be used to create sub-types from a given type definition.
Prohibited Substitutions (Applies to complex type definitions). Prevents sub-types that have been derived using the specified derivation methods from validating element instances in place of the given type definition.
Replace Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32).
Sequence Model Group Child elements and model groups must be provided in the specified order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-sequence.
Substitution Group Elements that are members of a substitution group can be used wherever the head element of the substitution group is referenced.
Substitution Group Exclusions (Applies to element declarations). Prohibits element declarations from nominating themselves as being able to substitute a given element declaration, if they have types that are derived from the original element's type using the specified derivation methods.
Target Namespace The target namespace identifies the namespace that components in this schema belongs to. If no target namespace is provided, then the schema components do not belong to any namespace.
Uniqueness Constraint Ensures uniqueness of an element/attribute value, or a combination of values, within a specified scope. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.